Phonics Rules by Age: A Complete Parent Guide to Reading Success (Jolly Phonics Aligned)
Parents often worry when they ask:
“My child is 5… should they already be reading?”
“Why does my child memorise words but struggle with new ones?”
“Which phonics rules are actually important by age?”
This guide answers those questions clearly, calmly, and correctly
Table of Contents
What Makes This Phonics Guide Different from Others?
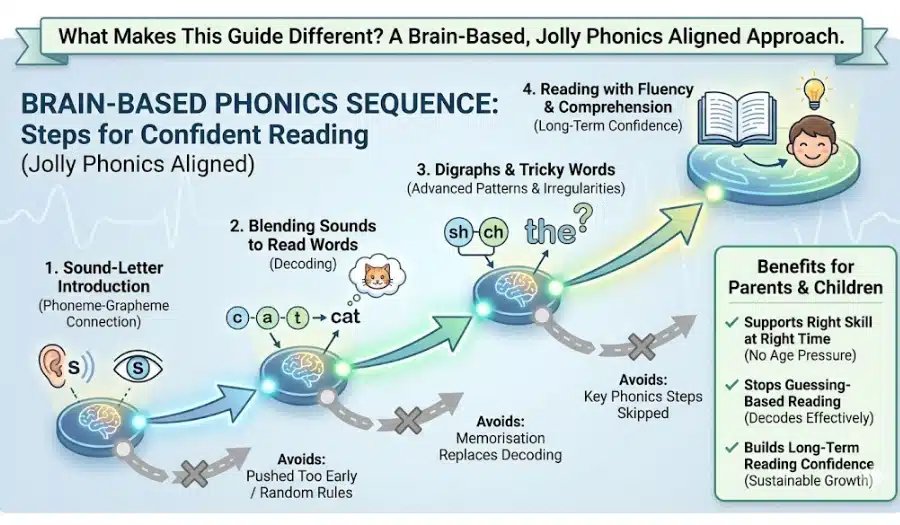
This guide follows a brain-based phonics sequence, avoids age pressure, and aligns fully with Jolly Phonics, rather than using random or rushed phonics rules.
Why That Matters
Most phonics problems happen because:
- Children are pushed to read too early
- Memorisation replaces decoding
- Key phonics steps are skipped
This guide helps parents:
- Support the right skill at the right time
- Stop guessing-based reading
- Build long-term reading confidence
Is Phonics Learned by Age or by Sequence?
Phonics is learned by sequence, not by age alone.
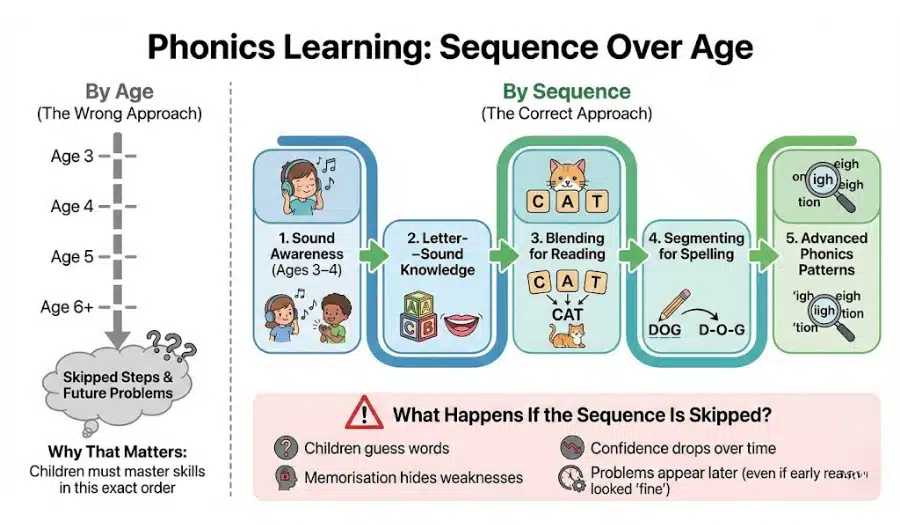
Why That Matters
Children must master skills in this exact order:
- Sound awareness
- Letter–sound knowledge
- Blending for reading
- Segmenting for spelling
- Advanced phonics patterns
What Happens If the Sequence Is Skipped?
- Children guess words
- Memorisation hides weaknesses
- Confidence drops over time
- Problems appear later (even if early reading looked “fine”)
👉 Read more → Why Guessing Words Is a Hidden Reading Problem
Ages 3–4: Pre-Phonics Stage (Listening Before Reading)

No. At ages 3–4, children should focus on listening and sound awareness, not reading words.
What Children SHOULD Learn
- Hearing rhymes (cat–hat)
- Clapping syllables (ba-na-na)
- Identifying beginning sounds
- Enjoying stories and songs
- Understanding words are made of sounds
Why This Stage Is Important
These skills prepare the brain for decoding later. Skipping this stage often leads to guessing habits.
🧠 Jolly Phonics Alignment
- Oral sound awareness only
- No pressure to read or spell
👉 Read more → Phonological Awareness Explained for Parents
Ages 4–5: Early Phonics Readiness (Sound–Letter Connection)
Should a 4–5-year-old be able to read words?
Answer:Not yet. Children aged 4–5 should learn letter sounds, not fluent reading.
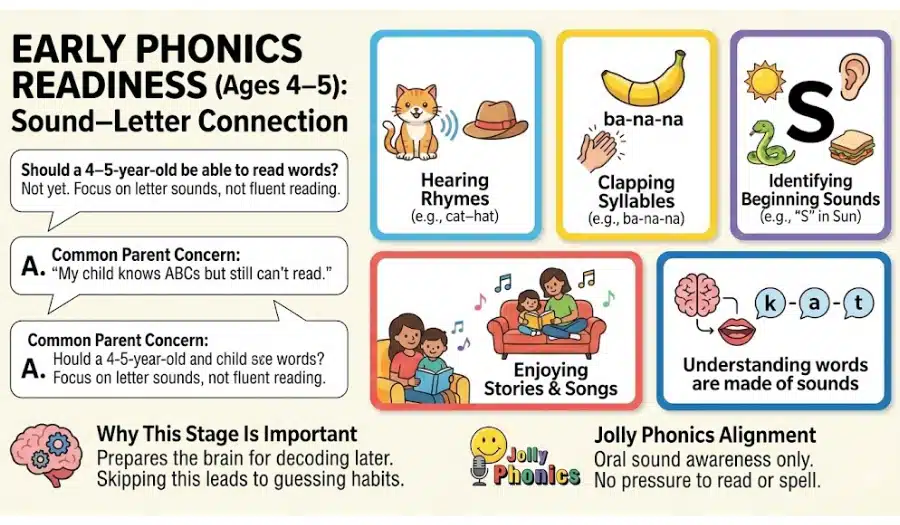
What Children SHOULD Learn
- Hearing rhymes (cat–hat)
- Clapping syllables (ba-na-na)
- Identifying beginning sounds
- Enjoying stories and songs
- Understanding words are made of sounds
Why This Stage Is Important
These skills prepare the brain for decoding later. Skipping this stage often leads to guessing habits.
🧠 Jolly Phonics Alignment
- Oral sound awareness only
- No pressure to read or spell
👉 Read more → Phonological Awareness Explained for Parents
Ages 5–6: Core Phonics Rules (Most Critical Stage)

What phonics rules should children know at ages 5–6?
Answer:Children aged 5–6 should learn to blend sounds to read and segment sounds to spell.
Skills Introduced
- One sound per letter (initially)
- Short vowels (a, e, i, o, u)
- CVC words (cat, pen, dog)
- Blending sounds to read
- Segmenting sounds to spell
Expected Outcomes
- Reads unfamiliar simple words
- Sounds out instead of guessing
- Spelling is phonetic (this is correct)
🧠 Jolly Phonics Alignment
- Systematic sound order
- Daily blending & segmenting
- Decodable books only
👉 Read more → Blending & Segmenting Made Simple for Parents
Ages 6–7: Expanding Phonics Knowledge

What new phonics skills do children learn at ages 6–7?
Answer:Children aged 6–7 learn phonics patterns that improve reading fluency and accuracy.
Patterns Introduced
- Long vowels (a-e, ee, ai)
- Digraphs (sh, ch, th)
- Blends (bl, tr, st)
- R-controlled vowels (ar, or, er)
- Common endings (-s, -ing, -ed)
👉 Read more → Long Vowels & Digraphs Explained with Examples
Ages 7–8: Advanced Phonics & Word-Attack Skills

Should phonics still be taught at ages 7–8?
Answer:Yes. At this stage, phonics helps children read longer and unfamiliar words confidently.
Skills Developed
- Diphthongs (oi, oy, ou, ow)
- Less common vowel teams (igh, ew)
- Syllable awareness
- Reading multi-syllable words
👉 Read more → How to Teach Syllable Reading Step by Step
Ages 8–9: Phonics Mastery & Fluency

What role does phonics play at ages 8–9?
Answer:By ages 8–9, phonics supports fluency, spelling, and comprehension, rather than being taught daily.
Skills at This Stage
- Soft c and g
- Irregular spelling patterns
- Homophones (there / their)
- Breaking long words into syllables
👉 Read more → When Phonics Becomes Automatic
Is Jolly Phonics Better Than Traditional Phonics?
Answer: Yes. Jolly Phonics uses a structured, multi-sensory approach that builds true decoding, not memorisation.
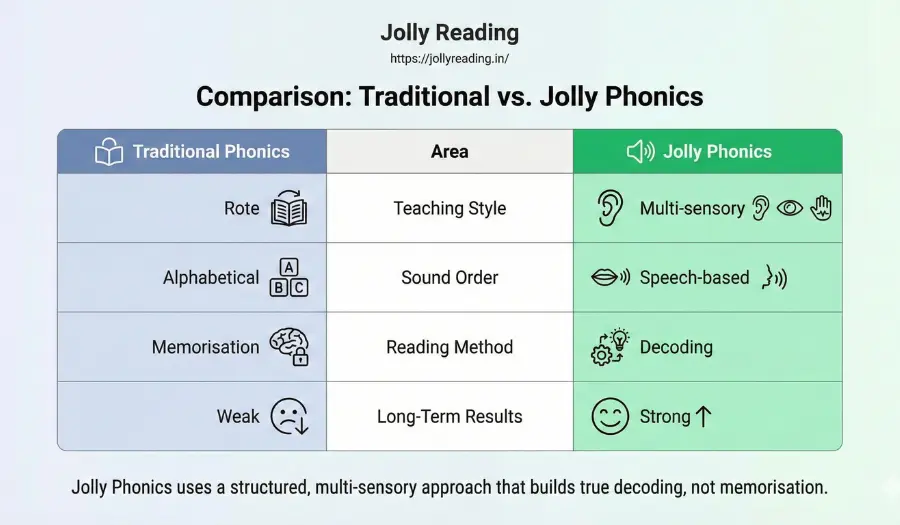
| Area | Traditional Phonics | Jolly Phonics |
|---|---|---|
| Teaching Style | Rote | Multi-sensory |
| Sound Order | Alphabetical | Speech-based |
| Reading Method | Memorisation | Decoding |
| Long-Term Results | Weak | Strong |
👉 Read more → Why Jolly Phonics Works Better Than Traditional Methods
Frequently Asked Questions About Phonics Rules by Age
Children usually begin phonics readiness between ages 4 and 5 by learning letter sounds. Formal phonics reading typically starts around ages 5 to 6 once sound awareness is strong.
Yes. At age 5, children are still developing blending and decoding skills. Fluent reading comes after these foundations are secure.
This often happens when phonics steps are skipped. Memorisation replaces decoding when children are pushed to read before mastering blending and segmenting.
Sound awareness, letter–sound knowledge, blending for reading, and segmenting for spelling are the most important early phonics skills.
If a child relies on pictures, first letters, or context instead of sounding out words, they are likely guessing rather than decoding.
Children should learn letter sounds first. Sounds help children read words, while alphabet names do not support decoding.
Yes. After age 7, phonics supports reading longer words, spelling accuracy, and overall reading fluency.
Yes. Structured phonics is especially effective for children who struggle with reading because it teaches skills step by step and reduces guessing.
Blending is combining sounds to read words, while segmenting is breaking words into sounds to spell. Both skills are essential for reading success.
Jolly Phonics is recommended because it uses a structured, multi-sensory approach that builds strong decoding skills and confident readers.
Short Summary
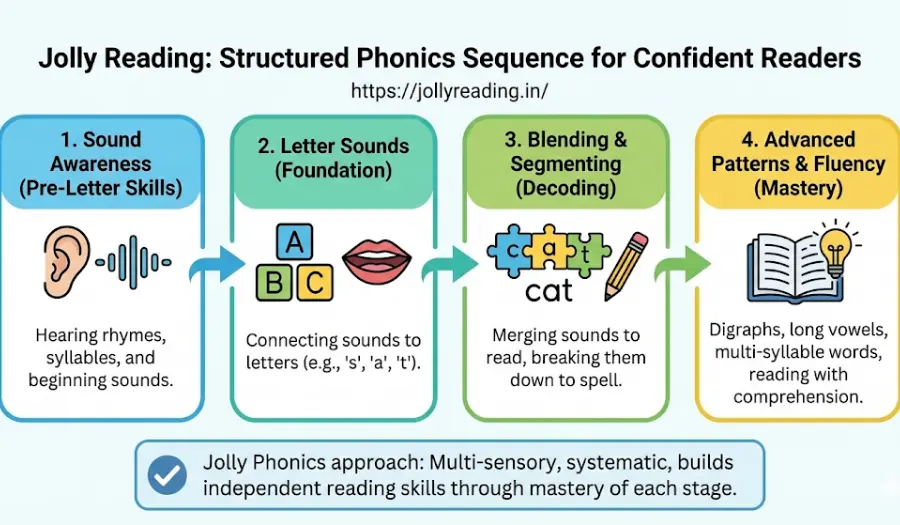
Phonics should be taught in a structured sequence, not rushed by age. Children progress from sound awareness to letter sounds, blending, and advanced patterns. Jolly Phonics uses a multi-sensory, systematic approach that builds confident, independent readers when each stage is mastered.

Megha Vyas
Founder of Jolly Reading with 23+ years of phonics teaching experience. Certified in Jolly Phonics and Jolly Grammar from Jolly Phonics CPD College, UK. Former Air India Air Hostess with expertise in phonetics, spoken English, and remedial education.







